This
course introduces learners to the principles, techniques, and applications of spot
welding, a resistance welding process widely used in sheet metal
fabrication and automotive manufacturing. It focuses on the operation of spot
welding machines, process parameters, material considerations, and safety
measures. Learners will acquire both theoretical knowledge and practical skills
in producing quality welds, identifying defects, and applying preventive
maintenance to spot welding equipment
- Teacher: GASPARD HARERIMANA
1. SMAW on Aluminum
-
Overview: Lightweight, highly conductive; difficult to weld due to oxide layer.
-
Electrodes: 4043, 5356 (AC).
-
Key Points: AC current needed, preheat thick sections, avoid excessive heat to prevent burn-through.
-
Applications: Repairs and maintenance when TIG is not available.
2. SMAW on Stainless Steel
-
Overview: Corrosion-resistant, retains high-temperature strength.
-
Electrodes: 308L, 309L, 316L.
-
Key Points: Low heat input, clean surfaces, multi-pass for thick sections.
-
Applications: Chemical, food processing, and construction industries.
3. SMAW on Cast Iron
-
Overview: Brittle, high carbon; prone to cracking.
-
Electrodes: Nickel-based (ENi-CI, ENiFe-CI).
-
Key Points: Preheat 300–600°C, slow cooling, mostly for repair work.
-
Applications: Repairing machinery, engine blocks, pipes

- Teacher: OLIVIER MPARIBATENDA
Assembling manufactured parts or components is the process of joining, fitting, or connecting individual parts that have been separately produced to create a complete product or subassembly. This process involves accurately aligning components, fastening them using methods such as screws, bolts, rivets, adhesives, or welding, and ensuring that the assembled product meets design specifications and functional requirements. Proper assembly ensures the product operates correctly, maintains durability, and achieves the intended performance.
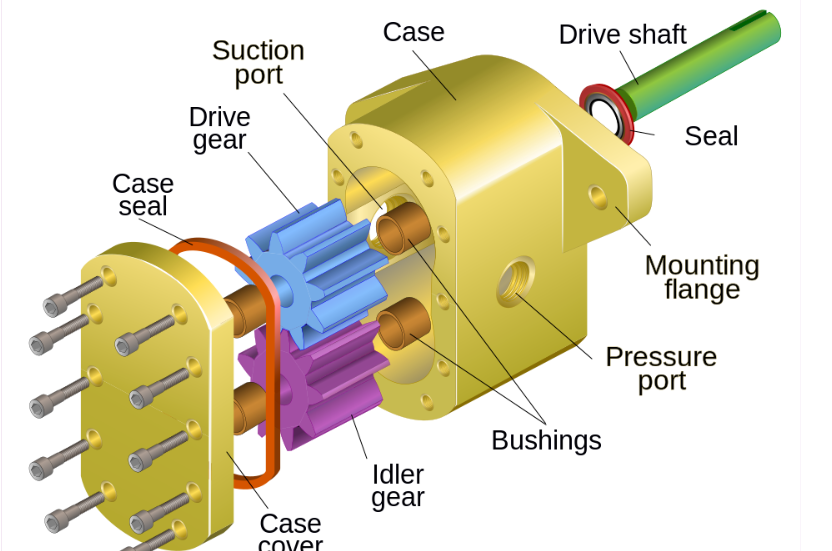
- Teacher: OLIVIER MPARIBATENDA
SOLIDWORKS Design is a computer-aided design (CAD) software used to create, simulate, and visualize 2D and 3D models of products or mechanical parts. It allows engineers, designers, and manufacturers to design complex components, assemblies, and drawings with precision and efficiency. The software provides tools for sketching, modeling, rendering, and analysis, enabling users to test product performance, optimize designs, and prepare accurate technical documentation before production.
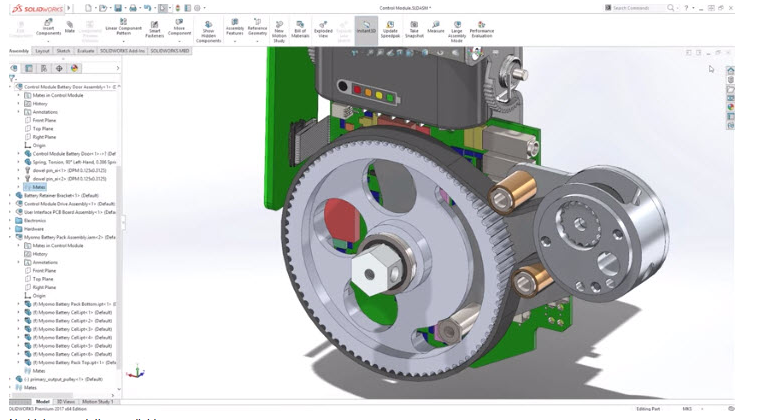
- Teacher: OLIVIER MPARIBATENDA
The course on Lathe Machine Operations introduces learners to the fundamental principles, components, and working of a lathe machine, one of the most versatile machine tools in manufacturing. The course emphasizes both theoretical knowledge and practical skills required for safe and efficient machining operations.
- Teacher: GASPARD HARERIMANA
Forging is a manufacturing process in which metal is shaped into the desired form by applying compressive forces using hammers, presses, or dies. The process is usually carried out at high temperatures (hot forging), but it can also be done at room temperature (cold forging). Forging improves the strength, toughness, and grain structure of the metal, making it suitable for producing strong and durable components like shafts, gears, bolts, and tools.

- Teacher: Paulin NIYIGABA
