CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines produce parts with high precision and repeatability by using programmed instructions. The process starts with a CAD model, which is converted into a CAM program that generates G-code and M-code to control tool movements, cutting speed, feed rate, and spindle rotation. Raw material fixed on a workholding device is shaped by cutting tools layer by layer into the final part, with operations such as milling, turning, drilling, and grinding often done in one setup. This method ensures accuracy, consistency, high productivity, and reduced human error, with finished parts inspected to meet quality and tolerance standards.
- Teacher: OLIVIER MPARIBATENDA
This course provides learners with the knowledge and practical skills required to install, operate, and maintain industrial machines safely and effectively. It covers the fundamental principles of machine installation, alignment, calibration, and commissioning, as well as preventive and corrective maintenance practices. Emphasis is placed on workplace safety, troubleshooting, and the application of industry standards to ensure reliability, efficiency, and longevity of machines used in industrial production.
- Teacher: GASPARD HARERIMANA
Pipe and pressure vessel welding is a specialized welding process used to join pipes and containers that are designed to hold fluids or gases under pressure. It requires high precision and strict quality standards to ensure strength, leak-proof joints, and safety under operating conditions.

- Teacher: Paulin NIYIGABA
Mechanical machines are devices that use physical components like gears, levers, and
pulleys to transform manual inputs into useful work.

- Teacher: Paulin NIYIGABA
Milling machines are versatile machine tools used to remove material from a workpiece by feeding it against a rotating cutter. They are widely applied in manufacturing for producing flat, curved, and irregular surfaces, as well as slots, gears, and complex shapes

- Teacher: GASPARD HARERIMANA
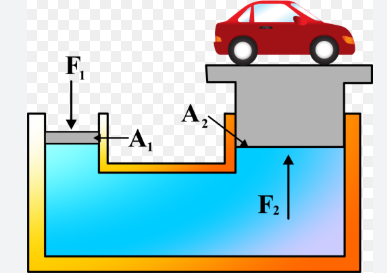
Basics of Hydraulic System
-
Definition: A hydraulic system is a power transmission system that uses pressurized liquid (usually oil) to transmit force and motion.
-
Principle: It works on Pascal’s Law, which states that pressure applied at one point of an enclosed fluid is transmitted equally in all directions.
-
Main Components:
-
Hydraulic pump (converts mechanical power into fluid power)
-
Valves (control pressure, flow, and direction)
-
Actuators (cylinders or motors that convert fluid power into mechanical motion)
-
Hydraulic fluid (medium for power transmission and lubrication)
-
-
Applications: Heavy machinery (excavators, presses), automotive brakes, aircraft systems.
-
Advantages: High force output, precise control, smooth operation.
Basics of Pneumatic System
-
Definition: A pneumatic system is a power transmission system that uses compressed air or gas to transmit and control energy.
-
Principle: It works on the compression and expansion of air; force is generated by pressurized air acting on a piston or actuator.
-
Main Components:
-
Compressor (supplies compressed air)
-
Valves (control air pressure, flow, and direction)
-
Actuators (pneumatic cylinders, air motors)
-
Air treatment units (filters, regulators, lubricators)
-
-
Applications: Automation in industries, packaging machines, air brakes, dental tools.
-
Advantages: Clean, lightweight, safe in hazardous environments, simple design.
- Teacher: OLIVIER MPARIBATENDA
Parts production on a CNC machine is the process of creating mechanical components by using computer-controlled tools to shape raw materials into finished products. It involves the use of CAD/CAM software to design the part, generate machining codes (G-code), and guide the CNC machine in executing precise operations such as cutting, milling, turning, drilling, and grinding.
The process begins with preparing the design, selecting suitable material, and setting up the machine with the required tools. Once the program is loaded, the CNC machine automatically performs machining operations with high accuracy, speed, and repeatability, producing parts that meet the required dimensions, tolerances, and surface finish.
CNC parts production is widely used in industries like automotive, aerospace, medical, and manufacturing, where consistency and precision are essential. It allows for mass production, reduced errors, and cost efficiency compared to manual machining.

