This course provides students with the knowledge and practical skills necessary to systematically observe, record, and interpret health and production data in livestock. Accurate record-keeping is crucial for effective herd management, disease control, genetic improvement, nutrition planning, and maximizing productivity.
The course focuses on the methods, tools, and significance of recording various parameters related to animal health, reproduction, growth, and production (milk, meat, eggs, etc.). Students learn how to maintain individual and herd-level records and use data for informed decision-making.

- Teacher: ALEXIE MUMUKUNDE
The course focuses on the production, improvement, and sustainable utilization of fodder crops and pastures. It covers establishment, management practices, conservation, pest and weed control, and rotational grazing. Learners gain skills to improve forage yield, maintain soil fertility, and ensure sustainable livestock feeding systems.

- Teacher: Jean Pierre RURANGIRWA
- Teacher: Jean Pierre RURANGIRWA
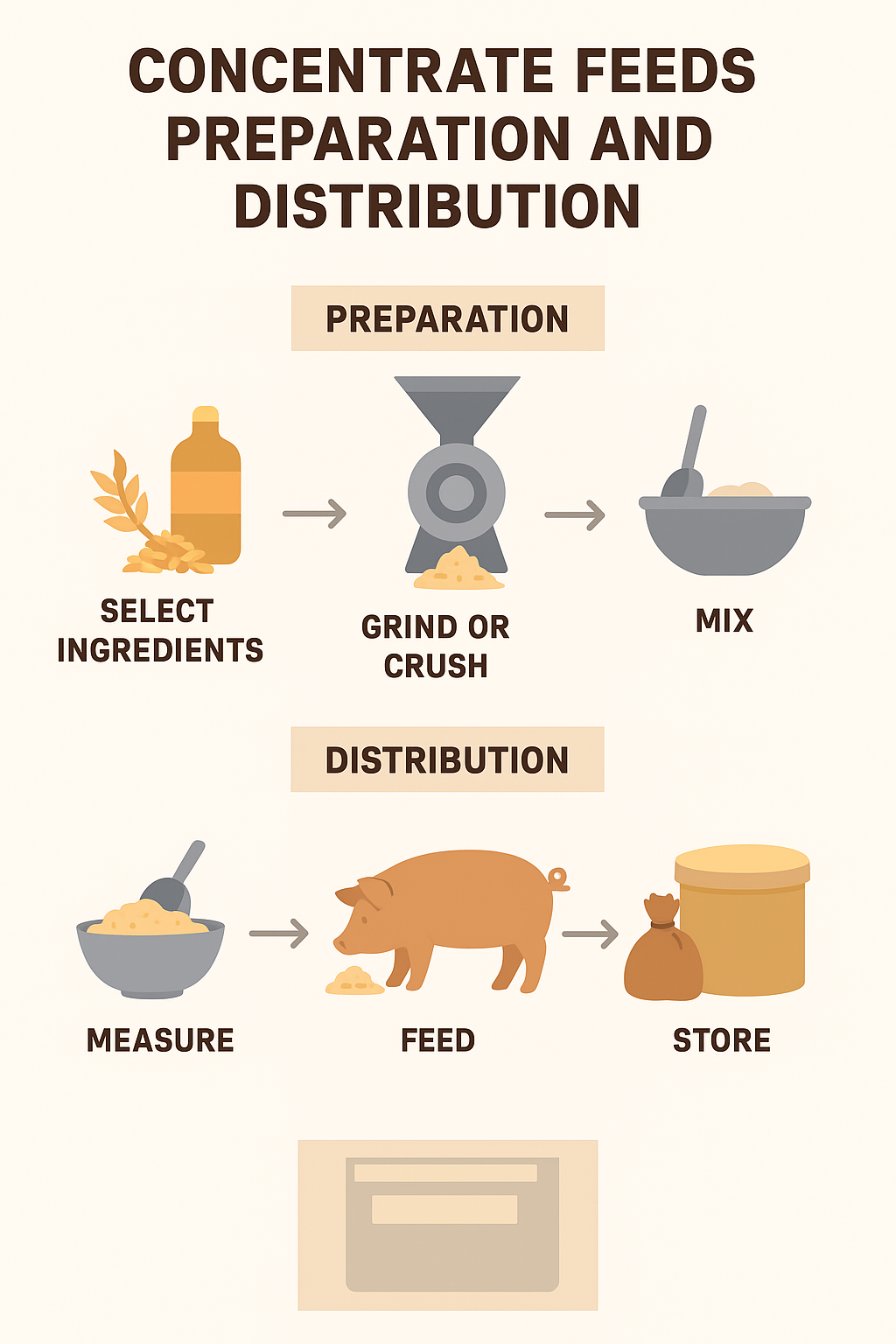
Concentrates are feeds rich in energy or protein, usually made from grains (like maize, sorghum), oilseed cakes (like soybean, groundnut), bran, and mineral–vitamin supplements. Their preparation involves selecting good-quality ingredients, grinding or crushing them for easy digestibility, mixing in the right proportions, and sometimes pelleting for easy handling.
Distribution of concentrates should be done according to the nutritional needs of the animals (species, age, weight, and production stage). They are usually given in measured amounts to avoid wastage, ensure uniform feeding, and prevent digestive disorders. Proper storage in dry, cool, and rodent-free areas is essential to maintain quality before distribution.
- Teacher: Jean Pierre RURANGIRWA
This course offers a complete guide to ruminant farming, broken down into five key learning outcomes.
It begins with Learning outcome 1, which focuses on the proper identification of common cattle, goat, and sheep breeds, detailing their unique physical and genetic characteristics.
Learning outcome 2 moves into practical farm management, covering the essential criteria for selecting a suitable site for ruminant shelters and identifying the appropriate construction materials and equipment needed for efficient operations.
Learning outcome 3 explains how to design shelters based on different production systems, from traditional to commercial.
The course then addresses animal health and productivity in Learning outcome 4, which outlines proper reproduction management, including breeding techniques, parturition assistance, and milk and weaning management.
Finally, Learning outcome 5 covers the nutritional needs of ruminants, providing guidance on feeding based on farming systems and managing common deficiencies to ensure animal health and optimal production.
- Teacher: ALEXIE MUMUKUNDE

