Search results: 215
This module introduces the foundational principles and elements essential to creating effective and visually appealing designs. It covers both theoretical concepts and practical applications.
- Teacher: Marie Chantal MASENGESHO
Bridge is the structure built to pass over different obstacles like rivers, road way ,valley, high way. The bridge superstructure are the following type like beam bridge, arch bridge, suspended bridge etc.
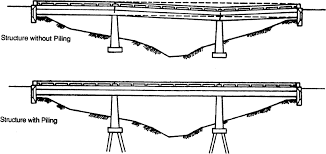
- Teacher: JEAN HAKIZIMANA
- Teacher: INNOCENT MUHAWENIMANA
- Teacher: Clemence MUKASHYAKA
- Teacher: Pierre MUNYAMBONERA,
This course provides learners with the knowledge and practical skills required to install, operate, and maintain industrial machines safely and effectively. It covers the fundamental principles of machine installation, alignment, calibration, and commissioning, as well as preventive and corrective maintenance practices. Emphasis is placed on workplace safety, troubleshooting, and the application of industry standards to ensure reliability, efficiency, and longevity of machines used in industrial production.
- Teacher: GASPARD HARERIMANA
This level focuses on the advanced skills and knowledge required to install, commission, maintain, and troubleshoot industrial machinery used in manufacturing environments. It covers mechanical, electrical, and control systems integration, emphasizing safety, efficiency, and compliance with industry standards.
- Teacher: AUGUSTIN MBONIGABA
JavaScript is a lightweight, flexible programming language that plays a central role in making web pages interactive. While it was originally designed to run only in browsers, today it also powers servers through platforms like Node.js.
At its core, JavaScript relies on variables to store and manage data. Developers can declare variables using var, let, or const. Of these, let and const are modern, block-scoped keywords, with const being used for values that should not be reassigned.
The language works with different data types, divided into two categories: primitives and reference types. Primitive values include strings, numbers, booleans, null, undefined, symbols, and big integers. Reference types, on the other hand, cover objects, arrays, and functions.
To manipulate data, JavaScript provides operators. These range from arithmetic operators for calculations, to comparison and logical operators for decision-making. Combining these with control flow structures, such as if...else statements and loops like for or while, allows developers to write logic that adapts to different situations.
Functions are another cornerstone of JavaScript. They let you group code into reusable blocks, which can be defined traditionally with the function keyword or in newer, more concise forms like arrow functions. Alongside this, objects and arrays make it possible to organize data: objects store information as key–value pairs, while arrays hold ordered lists of values.
One of JavaScript’s most powerful features is its ability to interact with the Document Object Model (DOM). Through the DOM, developers can dynamically update a webpage—changing text, styles, or structure in response to events. Events, such as a user clicking a button or pressing a key, can be captured and handled through event listeners, making websites more interactive and engaging.
In recent years, JavaScript has grown even more powerful thanks to modern ES6+ features. These include template literals for easier string formatting, destructuring for extracting values from objects or arrays, and the spread/rest operators for handling collections of data. JavaScript also supports modules, enabling code to be imported and exported across files, and provides asynchronous programming tools such as promises and async/await, which are essential for working with tasks like API calls or file operations.
The module discuss on variables, data types, operators, control flow, functions, objects, arrays, DOM manipulation, events, and modern ES6 feature used for the building blocks of interactive web development.

- Teacher: NDAGIJIMANA Silas
The course on Lathe Machine Operations introduces learners to the fundamental principles, components, and working of a lathe machine, one of the most versatile machine tools in manufacturing. The course emphasizes both theoretical knowledge and practical skills required for safe and efficient machining operations.
- Teacher: GASPARD HARERIMANA
This module describes the skills and knowledge required to prepare preliminary
activities for an Animal care technician, identify materials, tools and equipment
related to diagnosis and drug administration. It is intended for learners who have
successfully completed ordinary level, level II in animal health and its equivalent
and pursuing TVET level III and other related qualification. After that the trainees
will be able to use them, examine livestock diseases, take some types of samples
like feces, urine, milk, blood, pus, scabs, and use veterinary drugs after diagnosis
or in livestock diseases prevention. This module describes the process for using
tools, equipment and materials in different veterinary activities.

- Teacher: NIYONZIMA Fiston
Purpose statement
This module describes the skills and knowledge required to prepare preliminary
activities for an Animal care technician, identify materials, tools and equipment
related to diagnosis and drug administration. It is intended for learners who have
successfully completed ordinary level, level II in animal health and its equivalent
and pursuing TVET level III and other related qualification. After that the trainees
will be able to use them, examine livestock diseases, take some types of samples
like feces, urine, milk, blood, pus, scabs, and use veterinary drugs after diagnosis
or in livestock diseases prevention. This module describes the process for using
tools, equipment and materials in different veterinary activities.

- Teacher: Gilbert NZABANTERURA
Site Conditions means the physical and other conditions at the Site and the surrounding area as a whole, including conditions relating to the environment, transportation, access, waste disposal, handling and storage of materials, the availability and quality of electric power, the availability and quality of water, the availability and quality of roads, the availability and quality of labor personnel and local work and labor rules, climatic conditions and seasons, topography, air and water (including raw water) quality conditions, ground surface conditions, surface soil conditions, sound attenuation, subsurface geology, nature and quantity of surface and subsurface materials to be encountered (including Hazardous Materials), the geological and subsurface conditions of the Site, all other local and other conditions which may be material to Contractor’s performance of its obligations under the Agreement, and the location of underground utilities, obstructions and equipment and facilities needed before and during performance of Contractor’s obligations under the Agreement.

Metal cutting is the process of removing material from a metal workpiece to give it a desired shape, size, or surface finish. This is usually done using a cutting tool that shears away small chips of metal. Metal cutting is an essential operation in manufacturing industries to create parts and components for machinery, vehicles, and equipment.
There are two main

- Teacher: OLIVIER MPARIBATENDA
- Teacher: Basamiraho Emmanuel
This course will describe the skills and attitudes that will help the learners from level four animal health to acquire knowledge and attitude on milking equipment hygiene , milk cows , monitoring milk quality and quantity , perform minor maintenance of troubleshooting issues and finally communicate effectively with the milking parlor team.
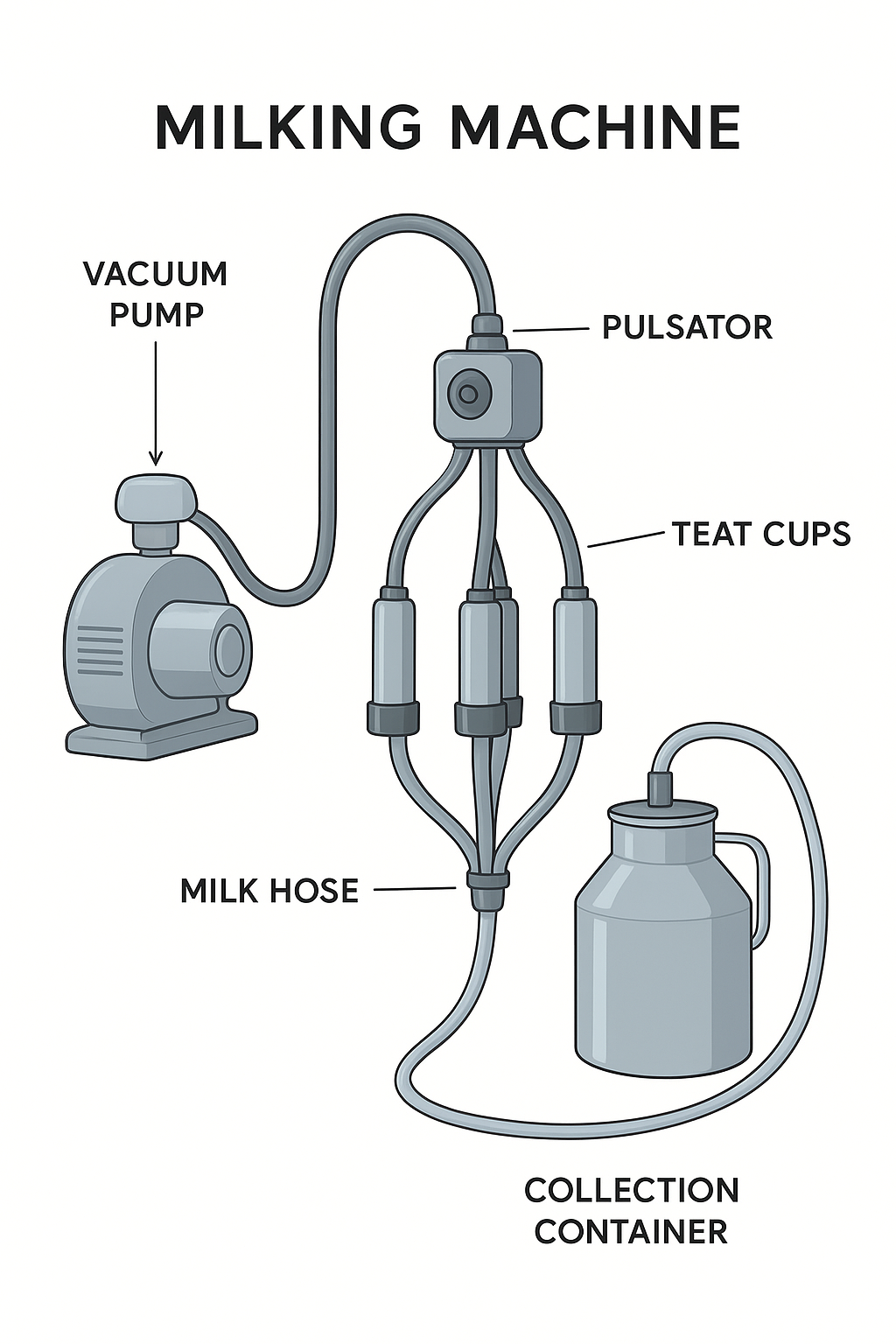
- Teacher: Olivier MUHOZA
- Teacher: INGABIRE Veronique
The Milling Machine Operations (MATMO501) module builds learners’ ability to organize, set up, and perform milling operations safely and efficiently. Key concepts include milling machine operation principles, workplace hazard control, product drawing interpretation, and preparation of materials, tools, and equipment. It also develops skills in setting mechanical components, adjusting milling parameters, and mounting workpieces for precision. Additionally, it emphasizes executing milling processes, inspecting and finishing milled parts, and integrating theoretical knowledge with practical application to ensure high-quality machine setup, operation, and quality assurance.
- Teacher: NIYITEGEKA Jean Damascene
This module describes
the skills knowledge and attitude required setup wireless network indoor. This
module is intended to prepare students pursing TVET Level 3 in Networking and
internet technology. At the end of this module the student will be able to apply
wireless network concepts, plan wireless network indoor installation, deploy
wireless network indoor and maintain wireless network indoor.
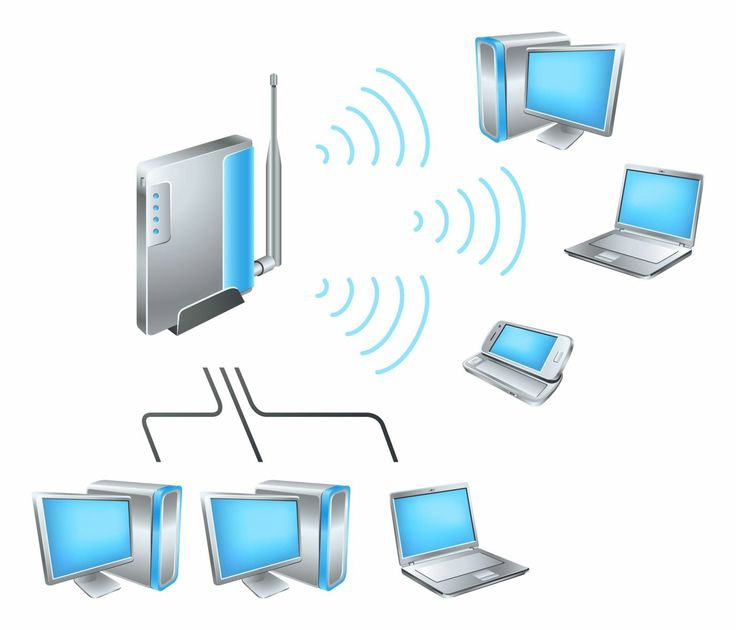

- Teacher: Origene IGIRANEZA
Course Summary: Ornamental Finishing Works
The course on Ornamental Finishing Works introduces learners to the principles, materials, and techniques used in enhancing the aesthetic and functional qualities of buildings through decorative finishes. It emphasizes practical skills and theoretical knowledge required to execute works such as plaster mouldings, cornices, terrazzo finishes, wall and ceiling decorations, floor finishes, and other ornamental treatments.
The module covers the identification and preparation of finishing materials, use of appropriate tools and equipment, surface preparation, and application techniques to achieve durable and visually appealing finishes. It also integrates aspects of measurement, cost estimation, safety, and quality standards in ornamental works.
By the end of the course, students will have the competence to interpret drawings and specifications, prepare work surfaces, apply decorative finishes, and maintain high standards of workmanship that align with both traditional and modern construction practices.
- Teacher: JACQUES NZAMUKWEREKA
Oxy-acetylene gas welding is a fusion welding process that uses a flame produced by burning acetylene (C₂H₂) with oxygen (O₂) to melt and join metals.
2. Equipment Used:
-
Oxygen cylinder (black)
-
Acetylene cylinder (maroon)
-
Pressure regulators
-
Hoses (red for acetylene, blue for oxygen)
-
Welding torch
-
Welding tips/nozzles
-
Spark lighter
-
Protective gear (goggles, gloves, apron)
3. Types of Flames:
-
Neutral flame (1:1 ratio of oxygen and acetylene) – used for most welding.
-
Carburizing flame (excess acetylene) – used for welding high-carbon steels and non-ferrous metals.
-
Oxidizing flame (excess oxygen) – used for brass, bronze, and certain steels.
4. Advantages:
-
Portable and versatile.
-
Low initial equipment cost.
-
Suitable for welding, cutting, brazing, and heating.
-
Ideal for thin metal sheets and maintenance work.
5. Disadvantages:
-
Not suitable for welding thick sections.
-
Slower than arc welding.
-
Generates lower temperatures.
-
Fire and explosion risks due to combustible gases.
6. Applications:
-
Sheet metal work
-
Automobile repairs
-
Plumbing and refrigeration
-
Metal sculpture and art
7. Safety Precautions:
-
Check for leaks before use.
-
Use in well-ventilated areas.
-
Never use oil or grease on regulators or fittings.
-
Keep cylinders upright and secured.
-
Follow correct lighting and shutdown procedures.

- Teacher: ALBERT IMANIRAFASHA
