Search results: 152
This module describes the skills, knowledge and attitude required to apply DevOps techniques. It is prepared for students pursuing TVET Level 5 in Software Development. At the end of this module the student will be able to Perform server configuration, Deploy the system and Implement monitoring strategies.
- Teacher: JeanBaptiste IRANKUNDA
This course equips TVET teachers with the knowledge and practical skills to design, facilitate, and assess inclusive blended learning using digital pedagogy, open educational resources, and innovative online tools.

- Teacher: HABIMANA Olivier
This module describes the skills, knowledge and attitude to be acquired by the learner to perform the domestic animal body description. The main contents of the module will help to describe the Animal body morphology using appropriate directional terms and planes. The module will also help to describe the body apparatus that makes the deep aspect of the animal body, thus this will lead to an assessment of the anatomo-physiological parameters of the main functions at the end of the module. A self-evaluation short quiz will provided during the presentation to evaluate your understanding regarding the contents of the module.

- Teacher: Olivier MUHOZA
A drilling machine operation is the process of creating, enlarging, or finishing holes in a workpiece using a rotating cutting tool called a drill bit. The machine works by rotating the drill bit at high speed while applying downward pressure to cut into the material. Common operations performed include drilling, reaming, counterboring, countersinking, tapping, and spot facing. Drilling machines are widely used in metalworking, woodworking, and construction due to their accuracy, efficiency, and ability to produce holes of different sizes and depths.
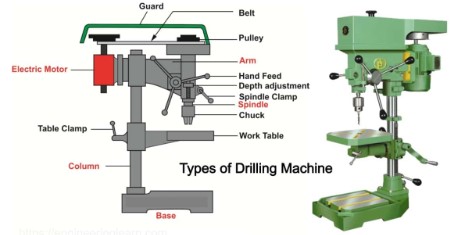
- Teacher: Paulin NIYIGABA
This module is intended for trainee at level 3 in TVET; certificate III, where trainee acquires skills, knowledge and attitudes to perform food and beverage service in hospitality industry. By the end of this module trainees will be able to receive instructions on the day’s activities and duties assemble and clean necessary restaurant equipment, arrange restaurant service areas set up the restaurant for service, stock the service station with minimum supervision.

- Teacher: Eric Hitimana
- Teacher: Origene IGIRANEZA
Fisheries and aquaculture. It is intended to the learners pursuing TVET Certificate
V in Animal health. Upon completion of this module the learners will be able to
Install aquaculture system, assist in hatching operations, perform nursery
activities, grow and harvest fishes.

- Teacher: Illuminee BARAKAGWIRA
This module detail required knowledge, skills
and attitude for student or learner to be able to feed fly record feeding data,
select fish feeds and manage feed requests and distribution. After learning
successively this module, a student or a learner will be able to work alone or
work in group under supervision.

This module covers the knowledge; skills and attitudes required to provide a balanced feeding to domestic animals by managing fodder crops and pasture in an optimum manner. It is intended for learners who have successfully completed ordinary level, level II in animal health or its equivalent and pursuing TVET level III and related qualification. Upon completion of this module, the trainee will be able to: Cultivate fodder crops, perform pastures lay out and improvement and Manage pasture grazing
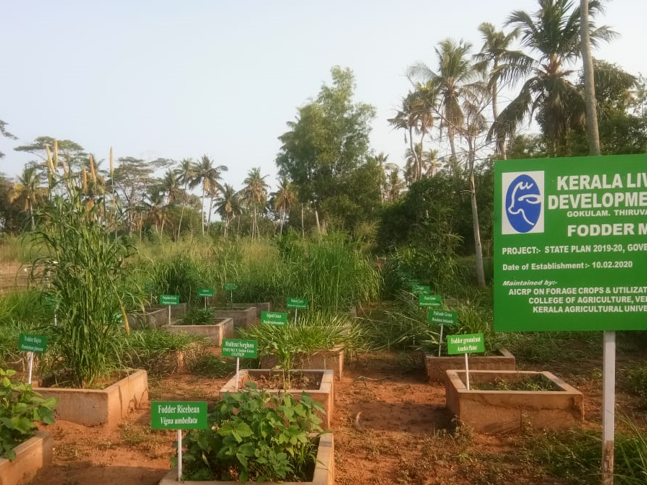

- Teacher: Patrick NGABONZIZA
This module covers the knowledge; skills and attitudes required to
provide a balanced feeding to domestic animals by managing fodder crops and
pasture in an optimum manner. It is intended for learners who have successfully
completed ordinary level, level II in animal health or its equivalent and
pursuing TVET level III and related qualification. Upon completion of this
module, the trainee will be able to: Cultivate fodder crops, perform pastures
lay out and improvement and Manage pasture grazing
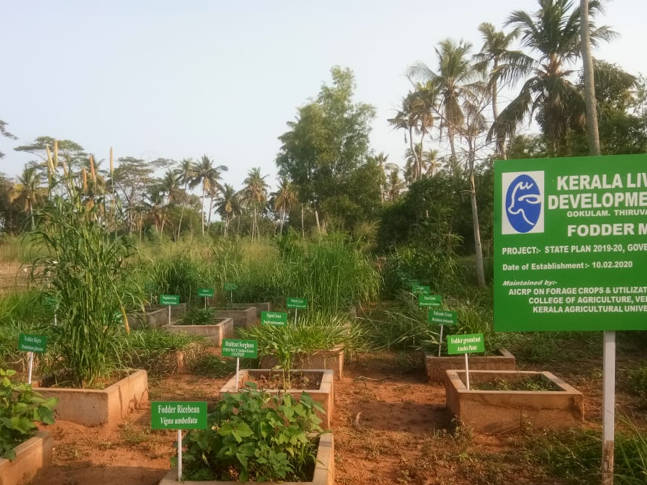

- Teacher: Callixte MATOVU
- Teacher: SadakoSandrine UMUKUNZI

- Teacher: INGABIRE Veronique
This module describes the skills, knowledge and attitudes required to identify history of food processing industry, identify food safety requirements and describe important processing operations in the food industry. At the end of this module, participants will be able to identify most important historical events of the transformation of cooked ingredients, by physical or chemical means into food, or of food into other forms. Learners will be able to improve food safety-related behaviours and practices. They can describe food processing activities such as mincing and macerating, liquefaction, emulsification, and cooking, pickling, pasteurization, and many other kinds of preservation and canning or other packaging.
- Teacher: Origene IGIRANEZA
This competence covers the skills, knowledge and attitude required to process fruits into Nectar and Squash in the food processing industry.
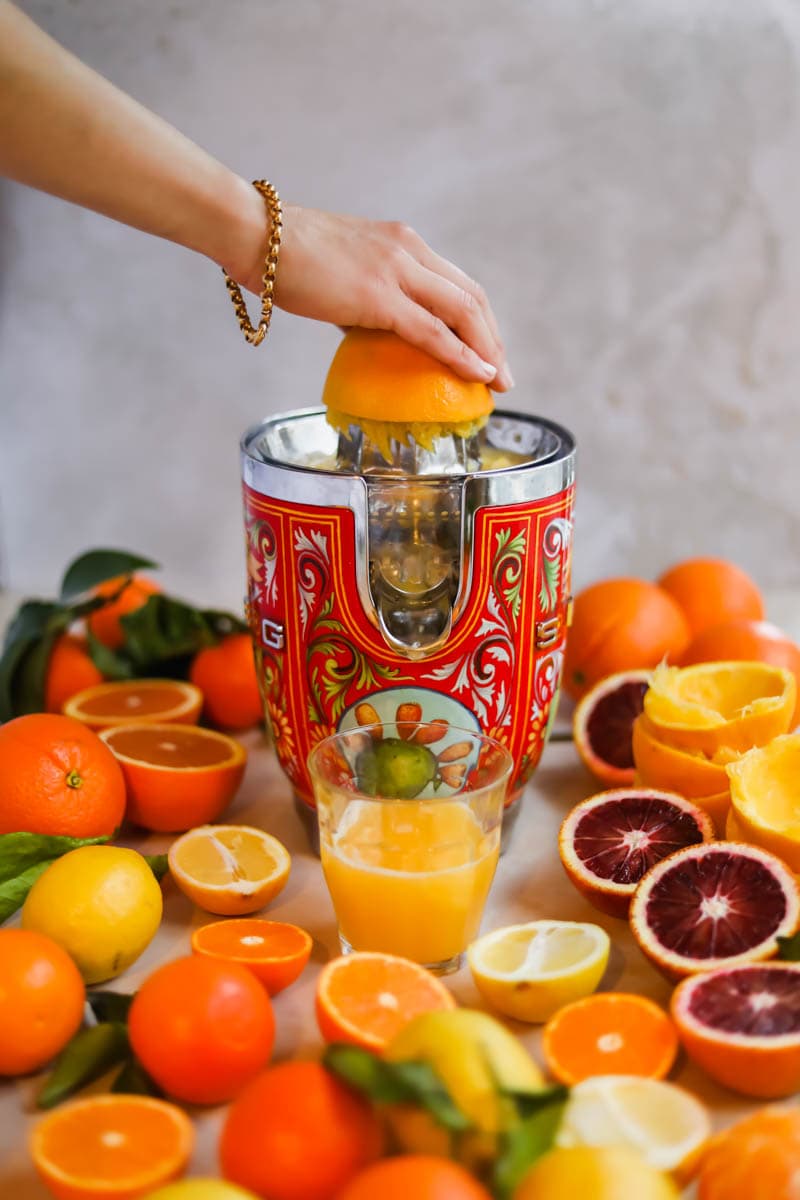

- Teacher: Eric Hitimana
- Teacher: Origene IGIRANEZA
Forging is a manufacturing process in which metal is shaped into the desired form by applying compressive forces using hammers, presses, or dies. The process is usually carried out at high temperatures (hot forging), but it can also be done at room temperature (cold forging). Forging improves the strength, toughness, and grain structure of the metal, making it suitable for producing strong and durable components like shafts, gears, bolts, and tools.

- Teacher: Paulin NIYIGABA
Forging is a metalworking process in which a piece of metal is shaped into the desired form by applying compressive forces, usually delivered through a hammer, press, or die. The operation is carried out while the metal is either hot (hot forging) or cold (cold forging), depending on the material and application.

Forging is a metalworking process where compressive forces are applied to shape metal, typically using a hammer or press. It improves mechanical properties by aligning the grain structure.
🔹 Purpose:
- To produce strong, durable parts
- Used in high-stress applications (e.g., automotive, aerospace, tools)
🔹 Types of Forging:
- Open-Die Forging
- Workpiece is compressed between flat dies
- Suitable for large or simple shapes
- Closed-Die Forging (Impression Die)
- Metal is compressed in a die cavity
- High precision and complex shapes
- Cold Forging
- Performed at room temperature
- Better surface finish, high dimensional accuracy
- Hot Forging
- Done above recrystallization temperature
- Easier to shape, less stress on equipment
🔹 Materials Used:
- Steel (carbon, alloy, stainless)
- Aluminum
- Titanium
- Brass and copper

- Teacher: ALBERT IMANIRAFASHA
Forging is a manufacturing process where metal is shaped by applying compressive forces using tools such as hammers, presses, or dies. The process can be performed at high temperatures (hot forging) or at room temperature (cold forging)

- Teacher: NIYITEGEKA Patrick

- Teacher: Eric Hitimana
- Teacher: Origene IGIRANEZA
The forest sector encountered a lot of challenges like forest seeds shortage in the markets. This module develops the skills and knowledge required to collect seeds. At the end of this module, the learner of level 3 will be able to select tools and equipment, identify tree species, apply seed collection and handle seed quality.

- Teacher: Eric Hitimana
- Teacher: Origene IGIRANEZA

