Search results: 152
- Teacher: Basamiraho Emmanuel
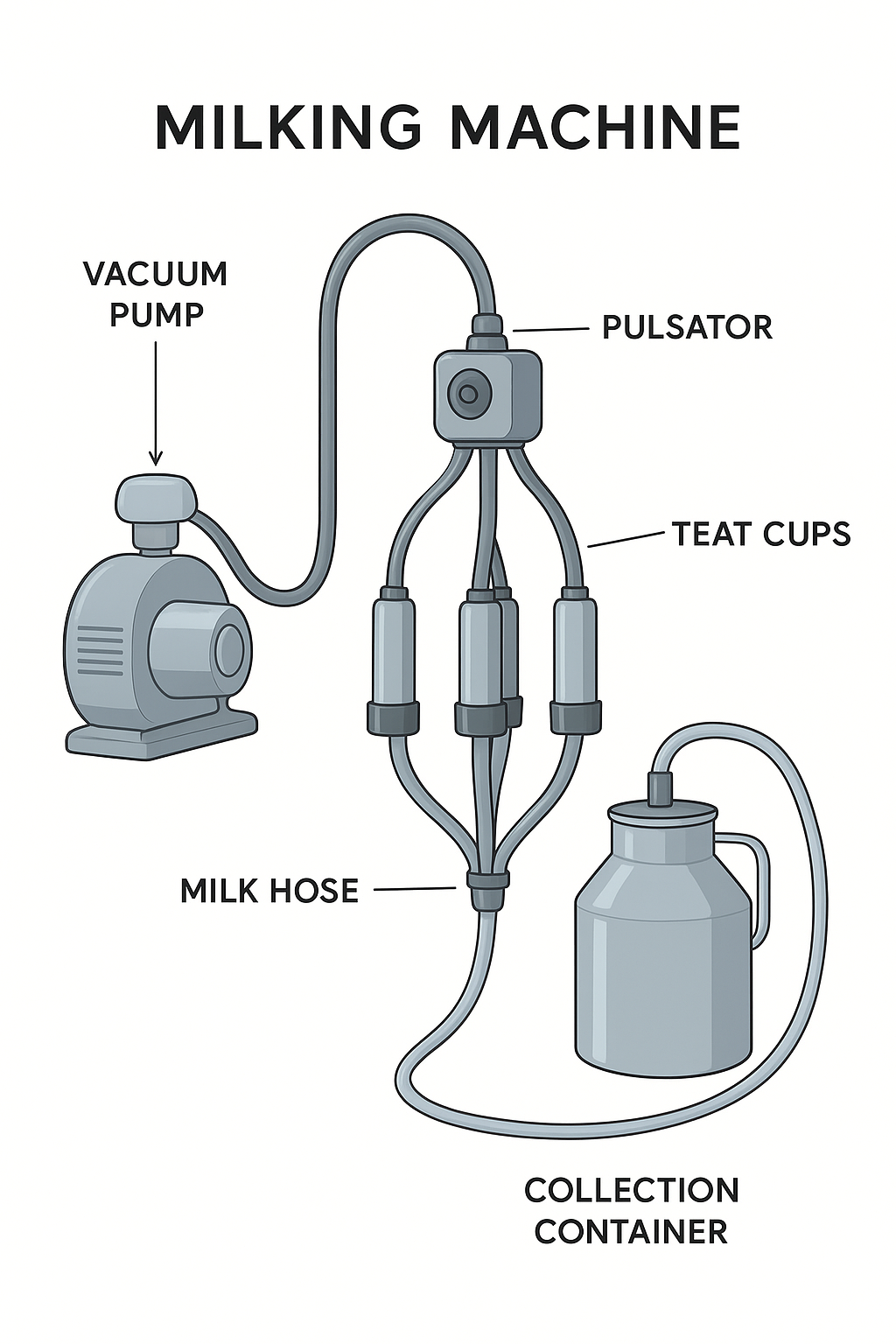
This course will describe the skills and attitudes that will help the learners from level four animal health to acquire knowledge and attitude on milking equipment hygiene , milk cows , monitoring milk quality and quantity , perform minor maintenance of troubleshooting issues and finally communicate effectively with the milking parlor team.
- Teacher: Olivier MUHOZA
- Teacher: INGABIRE Veronique
- Teacher: HAGENIMANA Eric
The minerals industry in the field of Underground Mine Design is presently faced with the problem of meeting a rapidly increasing domestic and foreign demand for its mineral resources. This increased demand has added to the problems already plaguing the industry increased land, labor, and material costs; increased foreign competition; more rigid Federal and State mining laws pertaining to health and safety; increased public awareness of air, stream, and land pollution; and increased public concern of mining practices and conditions within the mines.

- Teacher: Eric Hitimana
This module describes the knowledge and skills required for assisting to Necropsy evaluation. The module provide the essential for performing a pre-necropsy evaluation prior to necropsy procedures. The evaluation of body systems will be explained target the observation of macroscopic findings related to the cause of death. Before ending this module, you will be provided with essential knowledge that will help you to assist to laboratory sample analysis towards a decision of the Necropsy evaluation. Welcome to the module!
My name is MUHOZA Olivier, I am a Veterinary trainer at KISARO TSS. Allow me to introduce the module called NECROPSY EVALUATION (ANHNE503 as module code).This module describes the skills, knowledge and attitudes required to assist in
necropsy evaluation. At the end of this module, participants will be able to
perform pre-necropsy evaluation, assist in systemic evaluation and laboratory
analysis. Welcome to my module. THANK YOU!

- Teacher: Olivier MUHOZA
This module focuses on identifying, diagnosing, and managing animal parasites to promote animal health and productivity. It covers the major groups of parasites—helminths, arthropods, and protozoa—and their associated diseases.
1. Identification of Animal Parasites
Learners study the main classes of parasites:
-
Helminths – including nematodes, cestodes, and trematodes, described by their structure, lifecycle, and mode of infection.
-
Arthropods – such as insects, mites, and ticks, described by their morphology, development, and role as vectors.
-
Protozoa – single-celled parasites classified based on movement (flagella, cilia, pseudopodia) and mode of reproduction.
2. Description of Common Parasitic Diseases
Students learn about major parasitic diseases:
-
Helminthiasis – caused by parasitic worms like roundworms, tapeworms, and flukes.
-
Arthropod-borne diseases – caused or transmitted by ticks, flies, lice, and mites (e.g., anaplasmosis, babesiosis).
-
Protozoosis – caused by protozoan parasites such as Trypanosoma, Eimeria, and Babesia.
3. Diagnosis of Common Parasitic Diseases
The module trains students to:
-
Conduct clinical examinations following proper procedures.
-
Collect and handle samples (blood, feces, skin scrapings, etc.) according to protocols.
-
Examine samples using laboratory techniques (microscopy, flotation, staining).
-
Interpret results accurately based on clinical signs and lab findings.
4. Treatment and Control of Parasitic Diseases
Learners gain practical skills in:
-
Applying effective treatments specific to helminths, arthropods, and protozoa.
-
Monitoring animal health during and after treatment.
-
Implementing biosecurity and preventive measures such as sanitation, vector control, vaccination, and isolation to reduce disease spread.

- Teacher: NIYONZIMA Fiston
Parts production on a CNC machine is the process of creating mechanical components by using computer-controlled tools to shape raw materials into finished products. It involves the use of CAD/CAM software to design the part, generate machining codes (G-code), and guide the CNC machine in executing precise operations such as cutting, milling, turning, drilling, and grinding.
The process begins with preparing the design, selecting suitable material, and setting up the machine with the required tools. Once the program is loaded, the CNC machine automatically performs machining operations with high accuracy, speed, and repeatability, producing parts that meet the required dimensions, tolerances, and surface finish.
CNC parts production is widely used in industries like automotive, aerospace, medical, and manufacturing, where consistency and precision are essential. It allows for mass production, reduced errors, and cost efficiency compared to manual machining.

This course introduces learners to the principles and practices of producing mechanical parts using Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines. It covers the fundamentals of CNC machining, including the structure and functions of CNC machines, interpretation of engineering drawings, selection of tools and cutting parameters, and the preparation of CNC programs (G-codes and M-codes). Learners will develop skills in setting up workpieces, executing CNC operations such as turning, milling, and drilling, and applying quality control measures to ensure accuracy and precision of produced parts. The course also emphasizes safety practices, process optimization, and troubleshooting in CNC machining to prepare students for real-world manufacturing environments.

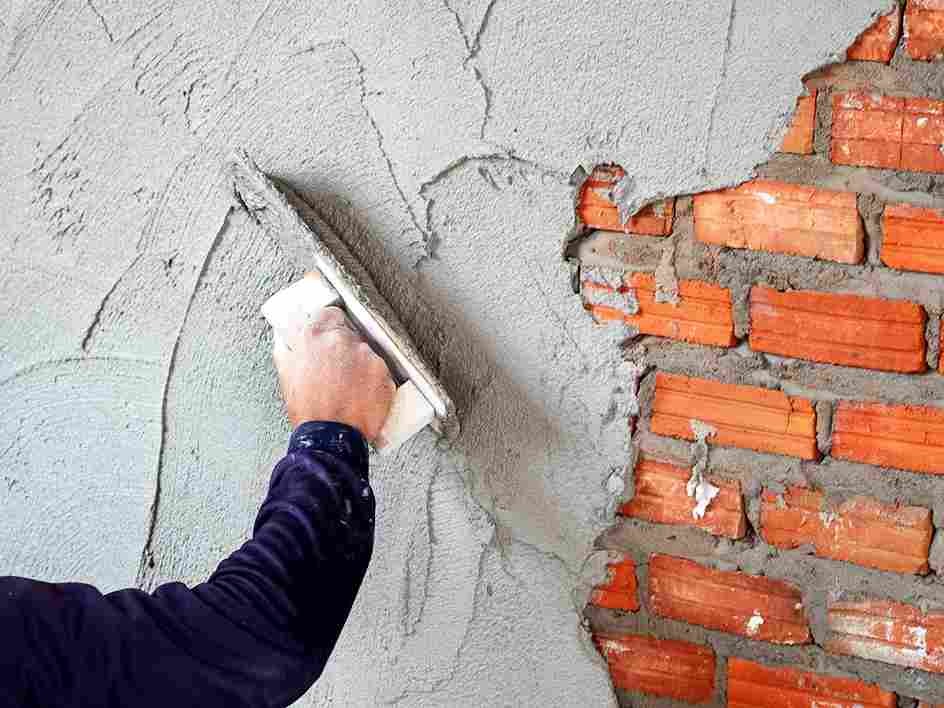
This is a core module which describes the skills, knowledge and attitude to be acquired by the learner to perform good work by preparing the working area and applying different coats in plastering in order to provide protection and good appearance of the wall at construction site and remove defects which may appear on the plastered walls. The learner deemed competent to this module may work at construction site in finishing stages under minimum supervision.
- Teacher: Jean Damascene TUYAMBAZE
Terrazzo is a composite material that originated in Italy during the 15th century.
It typically consists of chips of marble, quartz, granite, or glass mixed with a cement or epoxy binder.
The word “terrazzo” comes from the Italian word for terrace, as the original technique was used to create durable and decorative flooring in outdoor spaces.
- Teacher: Clemence MUKASHYAKA
This module is describes skills, knowledge and attitude, required to apply painting an artwork. At the end of the module the leaners will be able to prepare the working environment, paint the artworks and make the clear finishing of the artwork in respect of element and principles of painting.

- Teacher: Eric Hitimana
- Teacher: Origene IGIRANEZA
Pig farming operations involve the breeding, rearing, and management of pigs for meat (pork) and other by-products. The operations typically include housing and pen construction, feeding and nutrition management, breeding practices, health care and disease control, waste management, and marketing of pigs or pork products. Efficient pig farming focuses on providing proper housing, balanced feeding (concentrates and forages), hygiene, and veterinary care to ensure fast growth, high reproduction rates, and profitability.

- Teacher: Jean Pierre RURANGIRWA
This course equips learners with the knowledge and practical skills required to carry out welding on pipes and pressure vessels in accordance with industry standards and safety regulations. It covers the preparation of materials, selection of appropriate welding processes (such as SMAW, GTAW, and GMAW), setting of welding parameters, joint design, and defect prevention. Emphasis is placed on welding safety, handling of pressurized systems, and adherence to quality assurance procedures.
Inclusive methods such as demonstrations, guided practice, simulations, group projects, and blended learning are applied to ensure that all learners actively participate and develop confidence. Upon completion, learners will be able to perform high-quality welds on pipes and pressure vessels, interpret welding specifications, and ensure structural integrity and reliability in various industrial applications such as oil and gas, power plants, and manufacturing.

- Teacher: Jeremie NGIZWENAYO

- Teacher: Uwimbabazi Antoinette
- Teacher: JEAN HAKIZIMANA
- Teacher: Clemence MUKASHYAKA
- Teacher: Pierre MUNYAMBONERA,


