Search results: 152
This module describes the skills, knowledge and attitude required to repair car engine lubricating system. At the end of this module, learners will be able to identify, describe, repair and test car engine lubricating system components and test engine lubricating system under minimum supervision.

- Teacher: Origene IGIRANEZA
Sector: Transport and Logistic
Sub-sector: Automobile
- Teacher: Origene IGIRANEZA
Building a backend application often begins with designing a RESTful API using Express.js, a fast and minimal web framework for Node.js. REST (Representational State Transfer) provides a structured way of designing APIs, where resources are represented with endpoints and standard HTTP methods—GET for retrieving data, POST for creating new data, PUT/PATCH for updating existing data, and DELETE for removal. Express makes this process straightforward by offering simple methods to define routes, handle requests, and send responses. Middleware in Express can also be used to process data, log activity, or handle errors, making the development flow more modular.
Once the core API is built, the next step is ensuring the application is secure. Security involves protecting the API from common threats such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and cross-site request forgery (CSRF). Developers often use tools like Helmet.js to set secure HTTP headers, bcrypt for password hashing, and JSON Web Tokens (JWT) or OAuth for authentication and authorization. Validating user input, enforcing HTTPS, and rate limiting requests are additional best practices to reduce vulnerabilities and prevent misuse.
After development and securing the application, the final stage is deployment. Backend applications built with Express.js can be deployed on various platforms such as cloud services (AWS, Google Cloud, Azure), containerized environments using Docker, or platform-as-a-service providers like Heroku and Vercel. Deployment usually involves setting environment variables, connecting to production databases, and configuring process managers like PM2 to ensure the application runs continuously and can recover from crashes. Load balancers and scaling strategies are also applied to handle high traffic and maintain performance.
In short, RESTful API development with Express.js provides the foundation for handling client-server communication, securing the backend ensures reliability and protection against attacks, and deploying the application makes it accessible to real users in production environments. Together, these steps form the backbone of modern backend development.

- Teacher: NDAGIJIMANA Silas
The backend system design module introduces students to the principles and practices of designing server-side systems that power applications.
It focuses on how data is processed, stored, and retrieved efficiently using databases and server logic.
Students will learn how to design system architectures that ensure reliability, scalability, and security.
The module emphasizes practical skills in organizing system components and managing communication between client and server.
The backend system design module introduces students to the principles and practices of designing server-side systems that power applications.
It focuses on how data is processed, stored, and retrieved efficiently using databases and server logic.
Students will learn how to design system architectures that ensure reliability, scalability, and security.
The module emphasizes practical skills in organizing system components and managing communication between client and server.
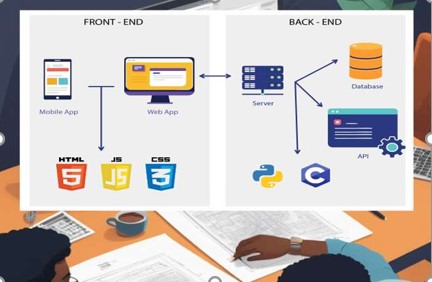
The backend system design module introduces students to the principles and practices of designing server-side systems that power applications.
It focuses on how data is processed, stored, and retrieved efficiently using databases and server logic.
Students will learn how to design system architectures that ensure reliability, scalability, and security.
The module emphasizes practical skills in organizing system components and managing communication between client and server.
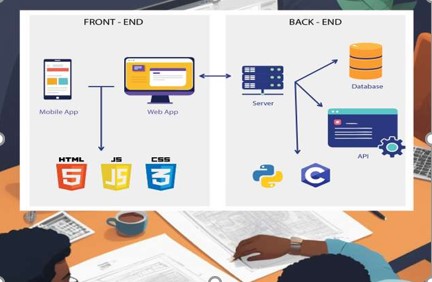
- Teacher: JeanDamascene BIMENYIMANA
- Teacher: KWIZERA INGABIRE DIANE
- Teacher: Wilson NIYONKURU
- Teacher: JULES NTIGURIRWA
Hydraulic Fluids:
-
Non-compressible fluids (usually oil) used to transmit power.
-
Operate using Pascal’s Law – pressure applied at one point is transmitted equally throughout the fluid.
-
Used for precise control and high force applications.
Pn eumatic Fluids:
eumatic Fluids:
-
Use compressed air or gas to transfer energy.
-
Compressible, so less precise than hydraulics.
-
Work on the principle of air pressure and flow – air expands to create motion.
-
Common in fast, light-duty operations.
- Teacher: AUGUSTIN MBONIGABA
Casting Process is a process in which hot liquid metal is poured into a mould that contains a hollow cut out or cavity of the desired finished shape. it is begins by creating a mould, which is the ‘reverse’ shape of the part we need. The mould is made from a refractory material, for example, sand. The metal is heated in an oven until it melts, and the molten metal is poured into the mould cavity. The liquid takes the shape of cavity, which is the shape of the part. It is cooled until it solidifies. Finally, the solidified metal part is removed from the mould.
- Teacher: Vedaste NDORUNKUNDIYE
Basics of Hydraulic System
-
Definition: A hydraulic system is a power transmission system that uses pressurized liquid (usually oil) to transmit force and motion.
-
Principle: It works on Pascal’s Law, which states that pressure applied at one point of an enclosed fluid is transmitted equally in all directions.
-
Main Components:
-
Hydraulic pump (converts mechanical power into fluid power)
-
Valves (control pressure, flow, and direction)
-
Actuators (cylinders or motors that convert fluid power into mechanical motion)
-
Hydraulic fluid (medium for power transmission and lubrication)
-
-
Applications: Heavy machinery (excavators, presses), automotive brakes, aircraft systems.
-
Advantages: High force output, precise control, smooth operation.
Basics of Pneumatic System
-
Definition: A pneumatic system is a power transmission system that uses compressed air or gas to transmit and control energy.
-
Principle: It works on the compression and expansion of air; force is generated by pressurized air acting on a piston or actuator.
-
Main Components:
-
Compressor (supplies compressed air)
-
Valves (control air pressure, flow, and direction)
-
Actuators (pneumatic cylinders, air motors)
-
Air treatment units (filters, regulators, lubricators)
-
-
Applications: Automation in industries, packaging machines, air brakes, dental tools.
-
Advantages: Clean, lightweight, safe in hazardous environments, simple design.
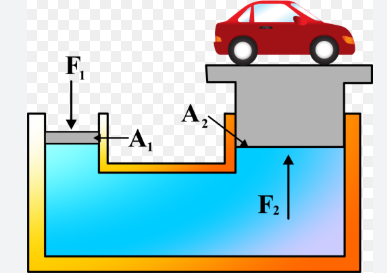
- Teacher: OLIVIER MPARIBATENDA
Technical drawing is a precise and detailed method of creating drawings that visually communicate how something functions or is constructed. It is commonly used in engineering, architecture, and manufacturing

- Teacher: OLIVIER MPARIBATENDA
This module describes the knowledge, skills and attitude required to create highly precise 2D designs that visualize construction drawings. It is intended to be delivered to learners pursuing TVET level IV in building construction. At the end of this module, the learner will be able to create, modify and plot construction drawings.
AutoCAD is a powerful and versatile software widely used in fields like architecture, engineering, and design for creating precise 2D and 3D drawings. This module introduces the fundamental concepts and tools of AutoCAD, providing a solid foundation for beginners. You will learn about the user interface, basic drawing and editing commands, layers, and how to manage and organize your work effectively. By the end of this module, you will be equipped with the essential skills to create simple, accurate designs and navigate AutoCAD’s core features with confidence. Whether you’re preparing for a career in design or simply looking to enhance your technical skills, this module offers the first step toward mastering AutoCAD.

- Teacher: Abel MURWANASHYAKA
This module introduces learners to AutoCAD software, a powerful Computer-Aided Design (CAD) tool used by engineers, architects, and designers to create precise 2D and 3D drawings.
- Teacher: Emmanuel HABIMANA
We are thrilled to welcome you to this module tailored specifically for students in building construction. This course is designed to provide you with a solid foundation in AutoCAD, a vital tool in the architecture, engineering, and construction industries.
In this module, you will learn the fundamental skills necessary to create accurate and detailed drawings that are essential for building design and construction. Our objectives include:
ü Understanding the AutoCAD interface and its key features specifically for building construction applications.
ü Learning to create and modify 2D drawings, including floor plans, elevations, and sections.
ü Developing skills in layering, dimensioning, and annotation to enhance your construction drawings.
ü Exploring basic 3D modeling techniques to visualize your designs effectively.
By the end of this module, you will be equipped to produce professional-quality construction drawings that meet industry standards.
We encourage you to actively participate in discussions and collaborate with your peers throughout the course. Your facilitator, [Instructor Name], is available at [Instructor Email] for any questions or support you may need.
Let’s embark on this journey together and master the basics of AutoCAD to advance your skills in building construction!
- Teacher: Theoneste HAKIZIMANA
- Teacher: Patrick KURAMBA
- Teacher: Onesphore MUHIRE
- Teacher: Marie Chantal MUKANEZA
- Teacher: Jeremie NSEKAMBABAYE
- Teacher: BLAISE PASCAL TURABUMUKIZA
This course introduces learners to the principles, components, and applications of hydraulic and pneumatic systems, which are widely used in manufacturing, engineering, and industrial automation. The course focuses on how fluids (liquids and gases) are applied in power transmission to generate force, motion, and control in machines
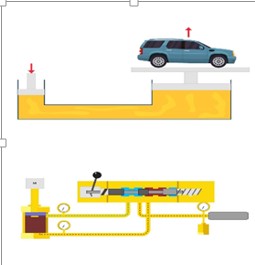
Hydraulic and pneumatic systems are both fluid power systems used in engineering and industry to transmit power and motion. They work by using a fluid as the medium to transfer energy from one point to another, enabling machines to perform useful work

- Teacher: NIYITEGEKA Patrick
Hydraulic and pneumatic systems are widely used in engineering and industry as power transmission methods. Both rely on fluids to transmit force and motion: hydraulics uses incompressible liquids (usually oil), while pneumatics uses compressible gases (usually air). Understanding these systems requires knowledge of their principles, components, and characteristics.
- Teacher: |GIRINSHUTI Fabrice
- Teacher: Emmanuel HABIMANA
- Teacher: Clemence MUKASHYAKA
- Teacher: JEANDAMASCENE NIYIBIZI
- Teacher: Jeremie NIYONSENGA
- Teacher: NIYITEGEKA Patrick
- Teacher: Theoneste SEMAJERI
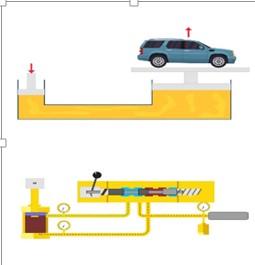
Hydraulic
and pneumatic systems are widely used in engineering and industry as power
transmission methods. Both rely on fluids to transmit force and motion:
hydraulics uses incompressible liquids (usually oil), while pneumatics uses
compressible gases (usually air). Understanding these systems requires
knowledge of their principles, components, and characteristics.
- Teacher: |GIRINSHUTI Fabrice
- Teacher: Emmanuel HABIMANA
- Teacher: NIYITEGEKA Jean Damascene
- Teacher: INNOCENT MUHAWENIMANA
- Teacher: Clemence MUKASHYAKA
- Teacher: Pierre MUNYAMBONERA,
- Teacher: JEANDAMASCENE NIYIBIZI
- Teacher: Jeremie NIYONSENGA
- Teacher: Theoneste SEMAJERI
This specific module describes the skills, knowledge and attitudes required to construct ceiling. Learners who successful completed level IV building construction and pursuing level V in building construction. This module students will be able to perform ceiling preliminary works, set out ceiling frame, construct ceiling frame and apply ceiling covering with minimum supervision.
- Teacher: Dieudonne TWIRINGIYIMANA
Beekeeping is the practice of managing and caring for honeybee colonies for the production of honey, beeswax, and other valuable products, as well as for crop pollination.
It is an important agricultural activity that supports both food security and environmental sustainability.
This course consists of 4 learning outcomes which are named as following:
1. Install Apiary
2. Keep honey bees
3. Harvest honey and honey bee product
4. Control honey bee diseases, pests and predators

- Teacher: JeanDamascene BIMENYIMANA
- Teacher: HAGENIMANA Eric
- Teacher: ALEXIE MUMUKUNDE
- Teacher: Jean Pierre RURANGIRWA
The Bench Work (MATBW301) module equips learners with the essential knowledge, skills, and attitudes required to perform accurate and safe bench work operations commonly used in manufacturing and mechanical engineering workshops. They will develop proficiency in handling hand tools, measuring instruments, and workshop equipment while adhering to occupational health, safety, and environmental standards. The course promotes problem-solving, attention to detail, and quality workmanship in producing components to specified dimensions and finishes.
- Teacher: NIYITEGEKA Jean Damascene
